
| Categories |
|---|
| Mechanics |
| Fluid Mechanics |
| Oscillation and Waves |
| Thermodynamics |
| Electricity and Magnetism |
| Optics |
| Modern Physics |
| Astronomy |
| Images |
|---|
 |
 |
 |
[Setup Time: 15 Min.] [Current Condition: Good]
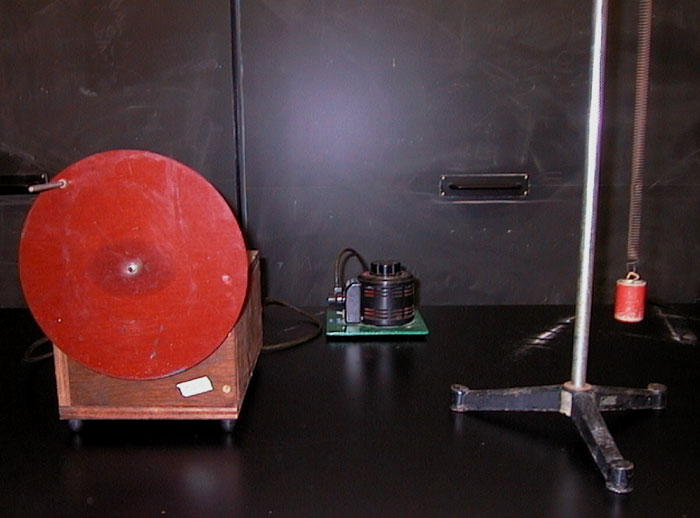
mass moves up and down on a spring; a peg moves up and down on a rotating circle; a light source projects their shadows onto a screen, and the superimposed images move in synchronized motion.
1. The easiest arrangement of the items is: point source, then mass and spring, then rotating circle (on the large blocks), and finally (of course) the screen. It's easier this way because when the mass is closer to the light source, its shadow is larger, and therefore you have a greater margin of error in trying to synchronize with the rotating circle.
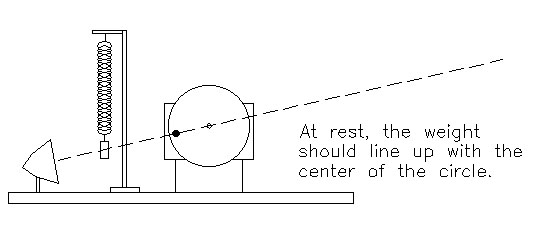
2. Once the items are set on the bench in this order, turn the point source on. Looking at the shadows on the screen, get things vertically aligned so the shadow of the disk is perfectly flat, and the mass is in line with the peg.
3. Next get things horizontally aligned: the peg should be rotated so that its shadow falls on the center of the disk.
4. Then the bar that the spring hangs from should be raised or lowered so that, at equilibrium, the mass is also in line with the peg and the center of the disk.
5. Now turn the variac on and set the disk rotating at a slow speed.
6. Pull the mass down so that its shadow overlaps with the lowest position of the peg: get ready and let go when they are perfectly overlapped.
7. Then watch the shadows and see whether the disk is moving too fast or too slow. Adjust the speed and repeat. This takes quite a bit of fine-tuning, and some practice timing when to release the spring.
Rotating Circle Device C. Oscillations, 2B
Variac L. Misc
Light Point Source L. Misc
2 Large Blocks in A. Mechanics, 1B
Pole Assembly by backwall
Spring in C. Oscillations, 1B
Mass in A. Mechanics, 1B
Screen by backwall
Demo Example:
N/A
N/A